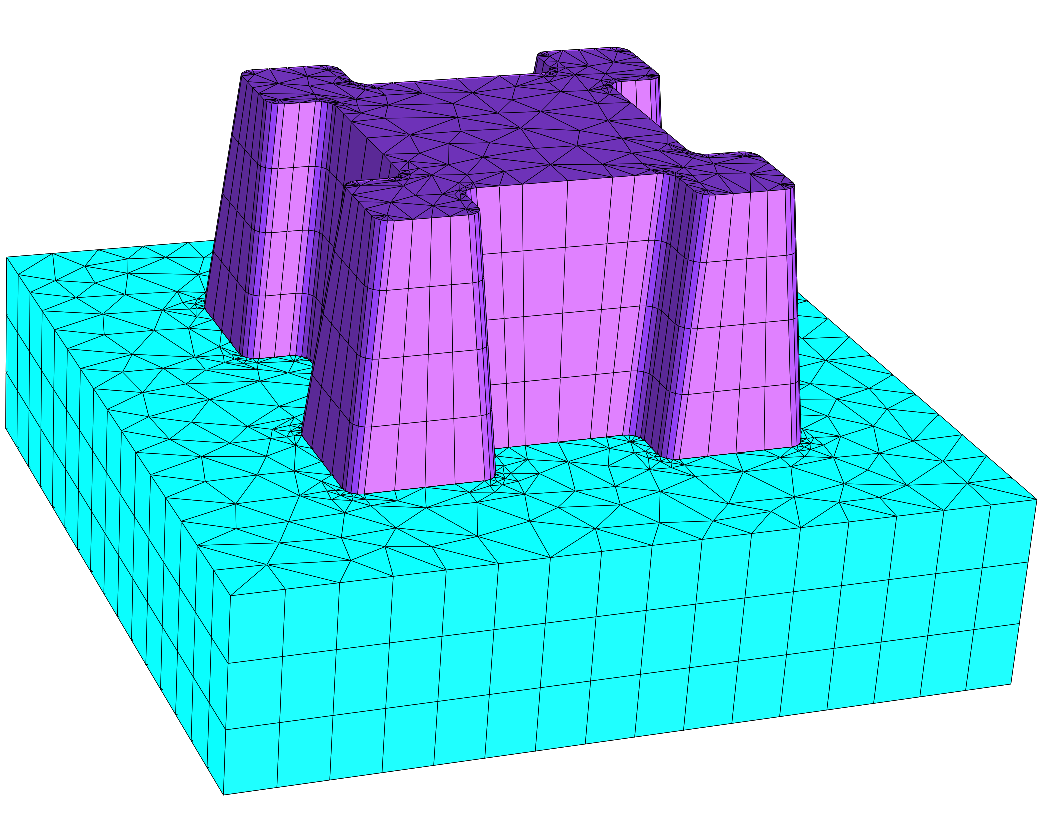
Boolean Union¶
Learning targets
- Construct object by Boolean operation (union)
- Apply shape transformations (normal displacement, corner rounding)
This example constructs a binary mask like square object with serifs at its corner. We apply corner roundings in the horizontal directions. Normal displacements are used to define oblique sidewall angles in  -direction.
-direction.
.jcm Input File
layout.jcm [ASCII]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102
Layout3D { UnitOfLength = 1e-09 MeshOptions { MaximumSideLength = 20 } Extrusion { Objects { Parallelogram { DomainId = 1 Priority = -1 Width = 200 Height = 200 Boundary { Class = Periodic } } BooleanOperation { DomainId = 2 Operator = Union A { Parallelogram { Height = 80 Width = 80 } } B { Parallelogram { Height = 32 Width = 32 GlobalPosition = [-40 -40] } Parallelogram { Height = 32 Width = 32 GlobalPosition = [40 -40] } Parallelogram { Height = 32 Width = 32 GlobalPosition = [40 40] } Parallelogram { Height = 32 Width = 32 GlobalPosition = [-40 40] } } NormalDisplacement = 0 CornerRounding { Radius = 4 NPoints = 5 } } } MultiLayer { MeshOptions { MaximumSideLengthZ = 20 } LayerInterface { BoundaryClass = Transparent } Layer { Thickness = 50 DomainId = 1 } LayerInterface { GeometryValues = [ BooleanOperation{1}/NormalDisplacement = -3 ] } Layer { Thickness = 65 DomainIdMapping = [1 2 2 3] } LayerInterface { GeometryValues = [ BooleanOperation{1}/NormalDisplacement = 3 ] } Layer { Thickness = 50 DomainId = 4 } } } }
Note
The mesh is constructed in a tensor-grid like manner (horizontal  -mesh
-mesh  vertical
vertical  -mesh). When deforming in
-mesh). When deforming in  -direction, the mesh quality depends on the cross-section mesh. For this we have chosen a zero normal displacement. This way the cross-section mesh corresponds to the geometry in middle for the structure.
-direction, the mesh quality depends on the cross-section mesh. For this we have chosen a zero normal displacement. This way the cross-section mesh corresponds to the geometry in middle for the structure.