Parameter Scan¶
With the parameterization of the test project in the previous section Keyword Substitution, it is straightforward to run a parameter scan within Matlab:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | %% holds computed scattering cross sections
scattering_cross_section_scan = [];
%% loop over radius values
for radius = [0.3 : 0.005 : 0.5]
fprintf('\nSolving for radius %5.2e', radius);
% set current parameter and solve the project
keys.radius = radius;
results = jcmwave_solve('mie2D.jcmp', keys, 'logfile', 'null');
scs = real(results{2}.ElectromagneticFieldEnergyFlux{1});
% gather results
scattering_cross_section_scan(end+1, 1 : 2) = [radius, scs];
end
%% plot scattering cross section against rod radius
radii = scattering_cross_section_scan(:, 1);
scs = scattering_cross_section_scan(:, 2);
plot(radii, scs, '-+', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('radius [\mu m]', 'FontSize', 14);
ylabel('integral scattering cross section', 'FontSize', 14);
set(gca, 'FontSize', 14);
|
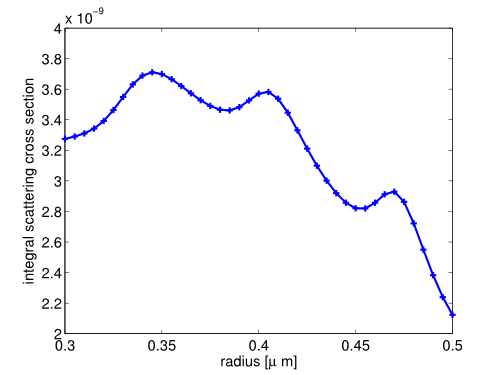
In line 2 we initialize the matrix scattering_cross_section_scan which later holds the computed data. In line 5 we start a loop over the rod radius. In each step the key-value container keys is updated with the current radius value (line 9), followed by a solver call (line 10). The optional parameter logfile redirects the solver console output to a file (using null disregards all console output). In line 15 we gather the relevant data. Line 19-24 serve the plotting of the results, see Figure “Scattering Cross Section”.
The next section Matlab Code Snippets demonstrates how to enrich the .jcmt input files with matlab scripts blocks.