DifferentialEvolutionOptimization¶
Purpose¶
The purpose of the driver is to identify a parameter vector 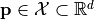 that minimizes the value of an objective function
that minimizes the value of an objective function 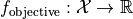 . The search domain
. The search domain 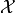 is bounded by box constraints
is bounded by box constraints 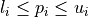 for
for 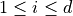 and may be subject to several constraints
and may be subject to several constraints 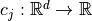 such that
such that 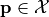 only if
only if 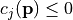 (see
(see create_study()).
The driver uses the heuristic evolutionary approach to search globally for a minimum of the objective function. We recommend to use Bayesian optimization to search globally for a minimum. Only if the evaluation times of the objective function are very short (smaller than 1-3 seconds) it can be beneficial to use differential evolution.
The implementation of the driver is based on the open source implementation of scipy (see https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.differential_evolution.html).
Usage Example¶
import sys,os
import numpy as np
import time
sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.getenv('JCMROOT'), 'ThirdPartySupport', 'Python'))
import jcmwave
client = jcmwave.optimizer.client()
# Definition of the search domain
domain = [
{'name': 'x1', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1.5,1.5)},
{'name': 'x2', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1.5,1.5)},
{'name': 'radius', 'type': 'fixed', 'domain': 2},
]
# Definition of a constraint on the search domain
constraints = [
{'name': 'circle', 'constraint': 'sqrt(x1^2 + x2^2) - radius'}
]
# Creation of the study object with study_id 'DifferentialEvolutionOptimization_example'
study = client.create_study(domain=domain, constraints=constraints,
driver="DifferentialEvolutionOptimization",
name="DifferentialEvolutionOptimization example",
study_id='DifferentialEvolutionOptimization_example')
# Definition of a simple analytic objective function.
# Typically, the objective value is derived from a FEM simulation
# using jcmwave.solve(...)
def objective(**kwargs):
time.sleep(2) # makes objective expensive
observation = study.new_observation()
x1,x2 = kwargs['x1'], kwargs['x2']
observation.add(10*2
+ (x1**2-10*np.cos(2*np.pi*x1))
+ (x2**2-10*np.cos(2*np.pi*x2))
)
return observation
# Set study parameters
study.set_parameters(max_iter=80, num_parallel=2)
# Run the minimization
study.set_objective(objective)
study.run()
info = study.info()
print('Minimum value {:.3f} found for:'.format(info['min_objective']))
for param,value in info['min_params'].items():
if param == 'x4': print(' {}={}'.format(param,value))
else: print(' {}={:.3f}'.format(param,value))
Parameters¶
The following parameters can be set by calling, e.g.
study.set_parameters(example_parameter1 = [1,2,3], example_parameter2 = True)
| max_iter (int): | Maximum number of evaluations of the objective function (default: inf) |
|---|
| max_time (int): | Maximum run time in seconds (default: inf) |
|---|
| num_parallel (int): | |
|---|---|
| Number of parallel observations of the objective function (default: 1) | |
| eps (float): | Stopping criterium. Minimum distance in the parameter space to the currently known minimum (default: 0.0) |
|---|
| min_val (float): | |
|---|---|
| Stopping criterium. Minimum value of the objective function (default: -inf) | |
| num_initial (int): | |
|---|---|
| Number of independent initial optimizers (default: 1) | |
| max_num_minimizers (int): | |
|---|---|
| If a minimizer has converged, it is restarted at another position. If max_num_minimizers threads have converged, the optimization is stopped (default: inf) | |
| sobol_sequence (bool): | |
|---|---|
| If true, all initial samples are taken from a Sobol sequence. This typically improves the coverage of the parameter space. (default: True) | |
| popsize_multiplier (int): | |
|---|---|
| A multiplier for setting the total population size. The population has popsize * len(x) individuals. (default: 15) | |
| tol (float): | The optimizer stops when the mean of the population energies (objective function values), multiplied by tol is larger than the standard deviation of the population energies. (default: 0.0) |
|---|
| strategy (str): | The differential evolution strategy to use. (default: best1bin) (options: [‘best1bin’, ‘best1exp’, ‘rand1exp’, ‘randtobest1exp’, ‘best2exp’, ‘rand2exp’, ‘randtobest1bin’, ‘best2bin’, ‘rand2bin’, ‘rand1bin’]) |
|---|
| mutation (float or tuple (min,max)): | |
|---|---|
Controls the mutation constant also known as differential weight, being denoted by F.If specified as a float it should be in the range [0, 2]. If specified as a tuple (min, max) dithering is employed. Dithering randomly changes the mutation constant on a generation by generation basis. The mutation constant for that generation is taken from U[min, max). Dithering can help speed convergence significantly. Increasing the mutation constant increases the search radius, but will slow down convergence. (default: (0.5, 1)) |
|
| recombination (float): | |
|---|---|
| The recombination constant, should be in the range [0, 1]. In the literature this is also known as the crossover probability, being denoted by CR. Increasing this value allows a larger number of mutants to progress into the next generation, but at the risk of population stability. (default: 0.7) | |