Displaying items by tag: quantum optics
Published in 2022
Published in 2022
Published in 2021
Published in 2020
Published in 2020
Published in 2018
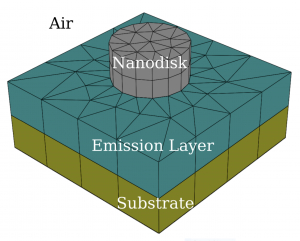
This post continues the series on modelling point dipole sources using reciprocity. It shows a concrete example of an ensemble of dipole emitters near a periodic nanostructure, which highlights the computational advantage of exploiting the receprocity theorem.
Published in Blog
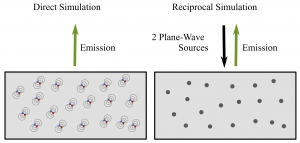
This post continues the series on modelling point dipole sources. This post extends the application of the reciprocity theorem to dipoles separated by a large distance. Furthermore, the benefits of the use of the reciprocity principle are discussed.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
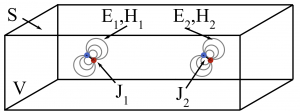
This post continues the series on modelling point dipole sources by discussing the application of the reciprocity principle to dipoles. In this post, the concept of reciprocity is introduced and applied to the near-fields of dipoles.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
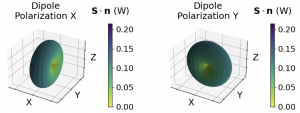
This is the second part of a series on dipoles. This post discusses how to evaluate the electromagnetic fields far away from the source. This is useful when modelling the spatial or angular distribution of light on a detector at a large distance form the source.
Published in Blog
Tagged under
Electric point dipole sources are, along with plane waves, one of the most commonly used sources types in electromagnetic computations. This first post on electric dipoles discusses their near-field properties both from both analytical expressions and numerical simulations in JCMsuite.
Published in Blog
Tagged under